
Allocating Joint Cost YouTube
In accounting, a joint cost is a cost incurred in a joint process. Joint costs may include direct material, direct labor, and overhead costs incurred during a joint production process. A joint process is a production process in which one input yields multiple outputs. It is a process in which seeking to create one type of output product.

PPT Cost Allocation Joint Products and Byproducts PowerPoint
Joint cost is the manufacturing cost incurred on a joint production process which takes common inputs but simultaneously produces multiple products called joint products e.g. processing of crude oil simultaneously yields gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, lubricants and other products.. In order to allocate costs to such joint products, accountants need to employ a suitable cost allocation method on.
PPT JointProcess Costing PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
The cost of this single input and the related manufacturing process costs are called joint costs 15. For example, lumber companies often must deal with joint products (different types of lumber) resulting from one input (a log). How do the concepts of joint products and joint cost help a lumber company establish a cost for each of its products?

PPT Cost Allocation Joint Products and Byproducts PowerPoint
A joint cost is a kind of common cost that occurs after a raw product, such as a sunflower crop, undergoes two separate production processes, reports Strategic CFO. For example, the cost of.
PPT JointProcess Costing PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
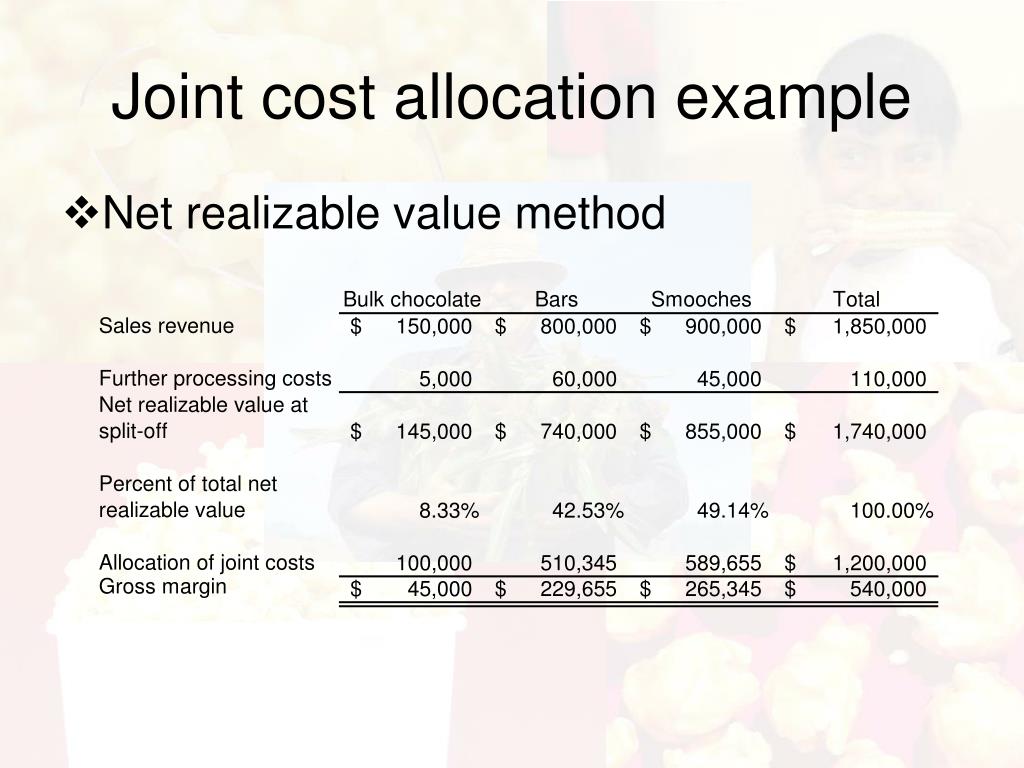
A cashew nuts processing unit produces two varieties of cashew nuts, premium and regular, at a joint cost of ₹75000, out of which ₹25000 is the fixed cost. The quantity produced is 100Kg and 150Kg; and sold at ₹750 and ₹600 per Kg, respectively. Apportion the joint cost using the contribution margin method. Solution:
PPT Cost Allocation Joint Products and Byproducts PowerPoint
Example: Joint products A, B, C, and D are produced at a total joint production cost of $120,000. The following quantities are produced: A, 20,000 units. B, 15,000 units. C, 10,000 units. D, 15,000 units. Additionally, product A sells for $0.25, B for $3.00, C for $3.50, and D for $5.00. These prices are market or sales values for the products.
PPT Cost Allocation Joint Products and Byproducts PowerPoint
The joint cost should not be confused with the common cost because they are significantly different from each other. A true joint cost is always indivisible whereas a common cost is divisible. In case of common cost, the products or services can be obtained separately and any shared or common cost incurred to obtain the products and services.

Joint Cost
Formulated with evidence-based doses of patented Curcumin C3 Complex, FruiteX-B, Boswellin Super, UC-II Collagen and Bioperine. Promotes healthy joint integrity, eases inflammation and fights.
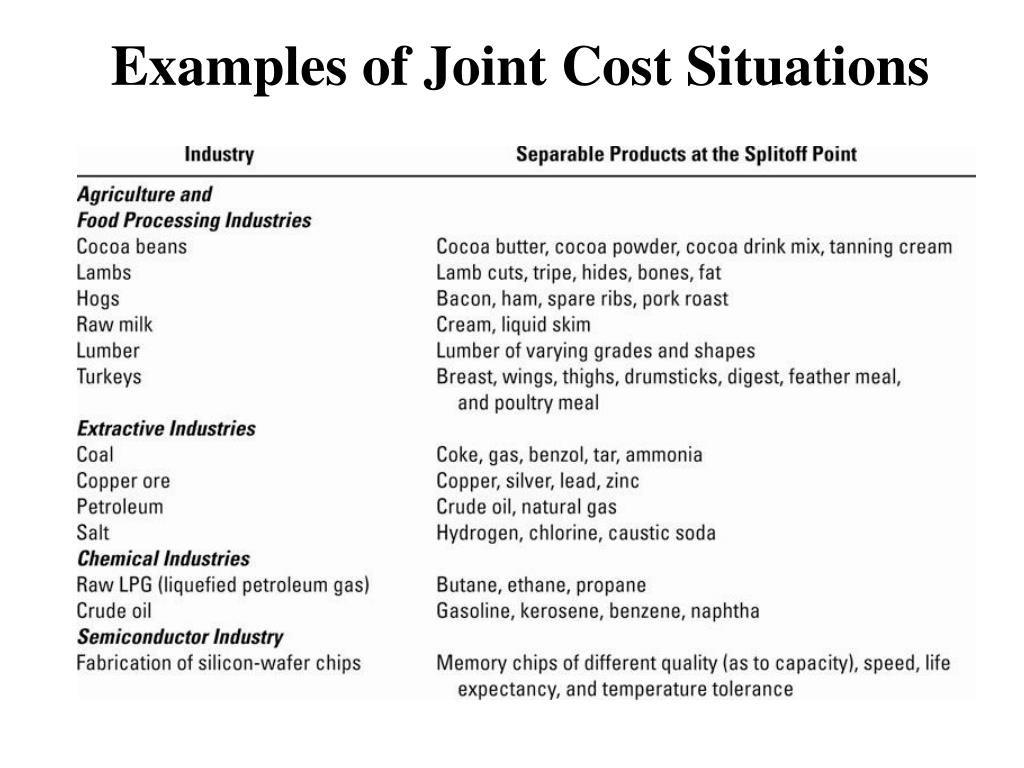
PPT Chapter 16 Joint Cost s PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Joint cost. Manufacturers incur many costs in the production process. It is the cost accountant's job to trace these costs back to a certain product or process (cost object) during production. Some costs cannot be traced back to a single cost object. Some costs benefit more than one product or process in the manufacturing process.
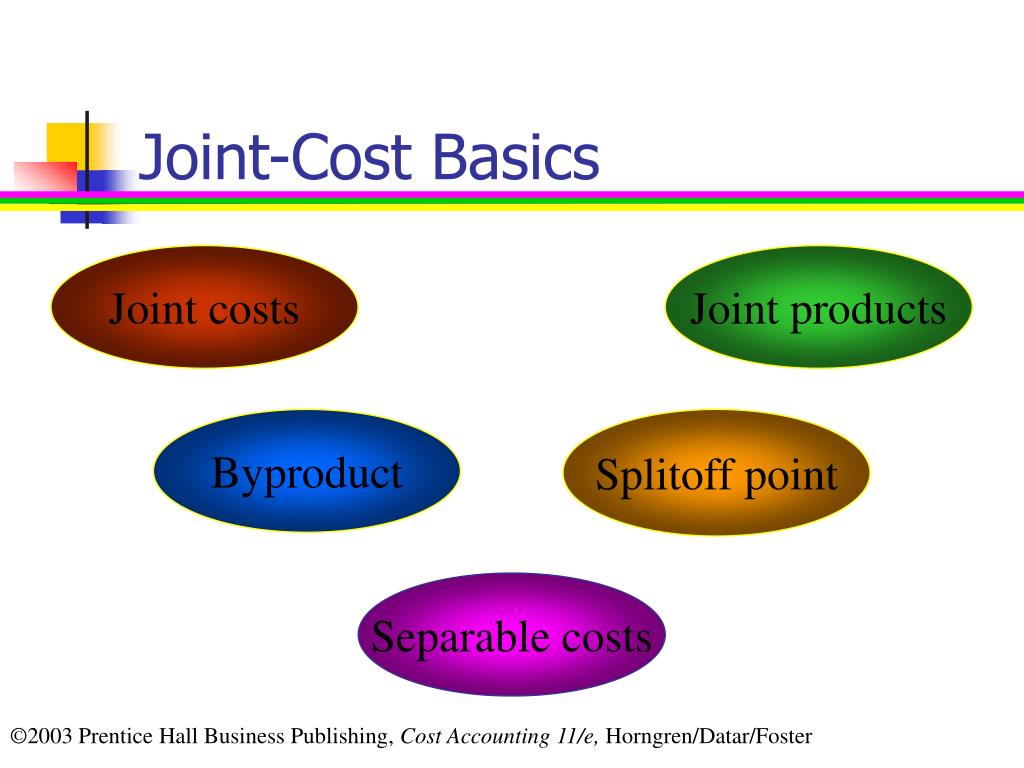
PPT Cost Allocation Joint Products and Byproducts PowerPoint
An anti-inflammatory eating pattern over the years may cut your risk of gout by as much as 60%, says McCormick. A steady diet of anti-inflammatory foods may also help to reduce joint pain for people living with osteoarthritis and potentially slow the progression of damage. To get the most benefit you've got to eat a variety of anti.
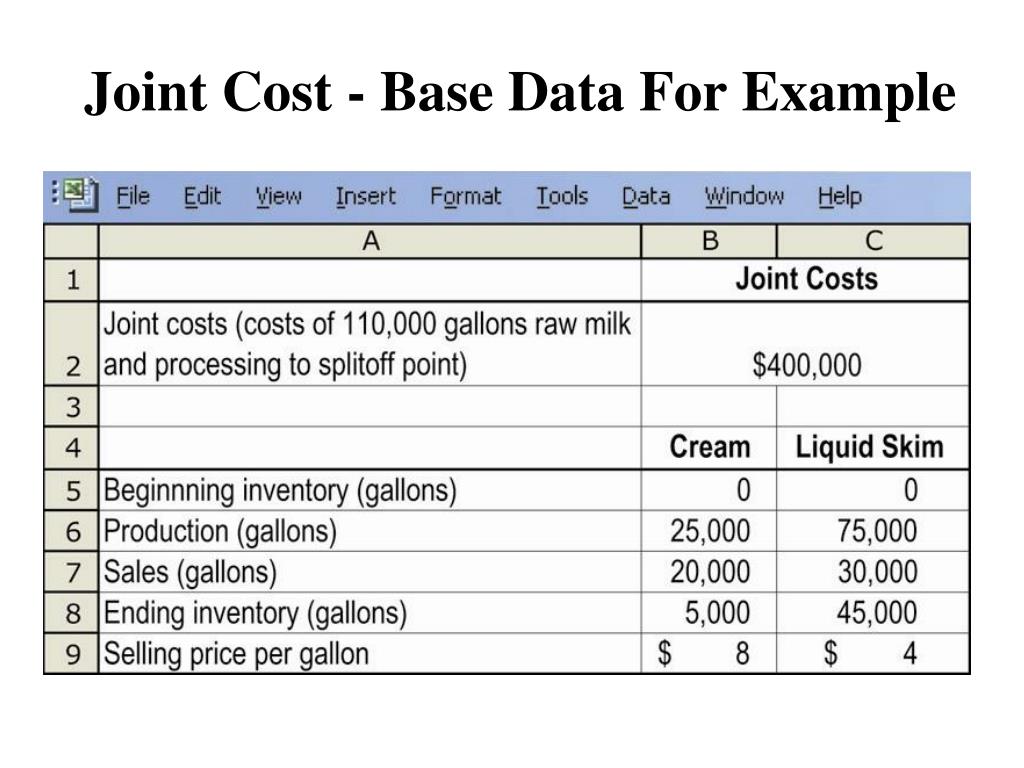
PPT Chapter 16 Joint Cost s PowerPoint Presentation, free download
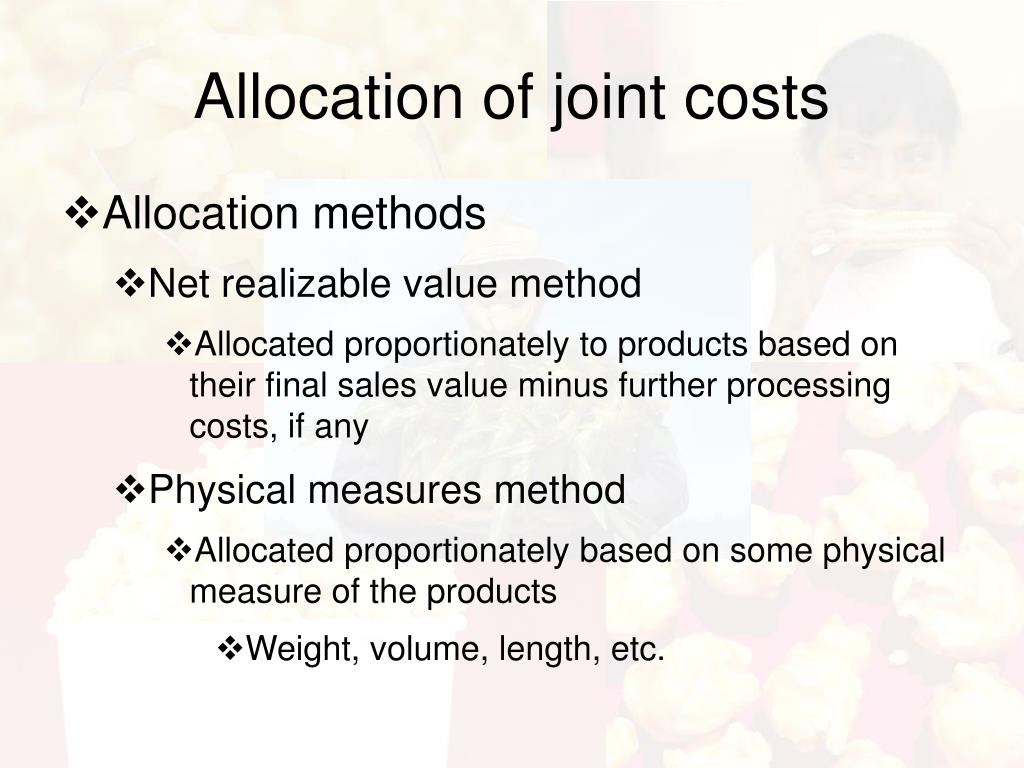
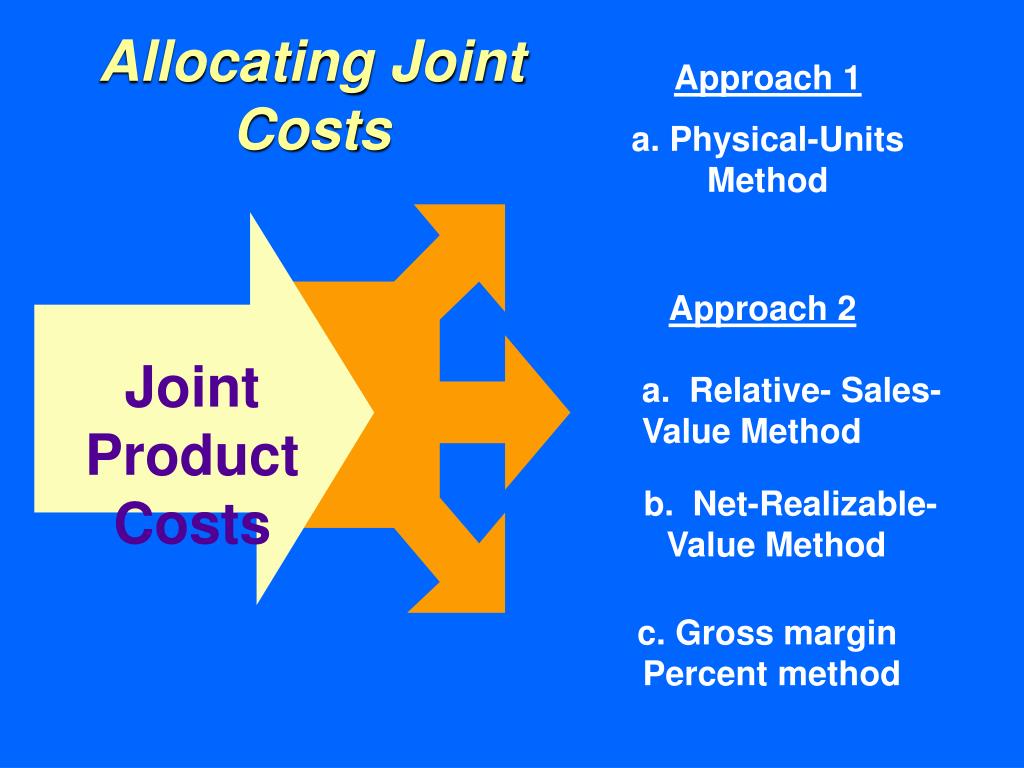
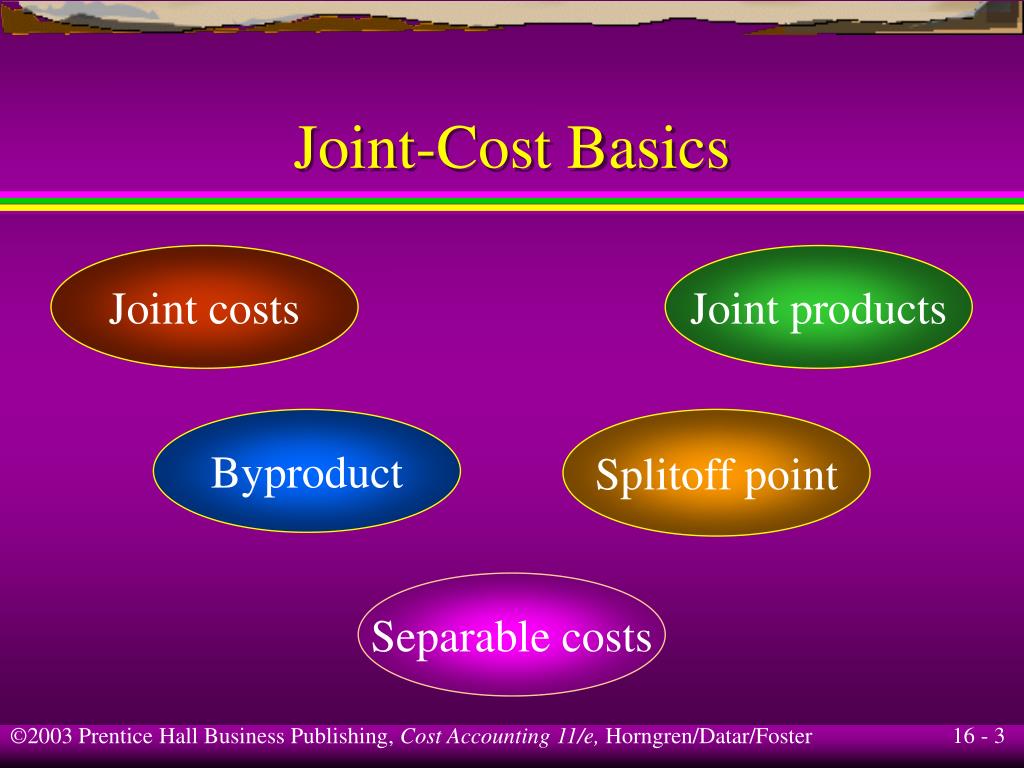
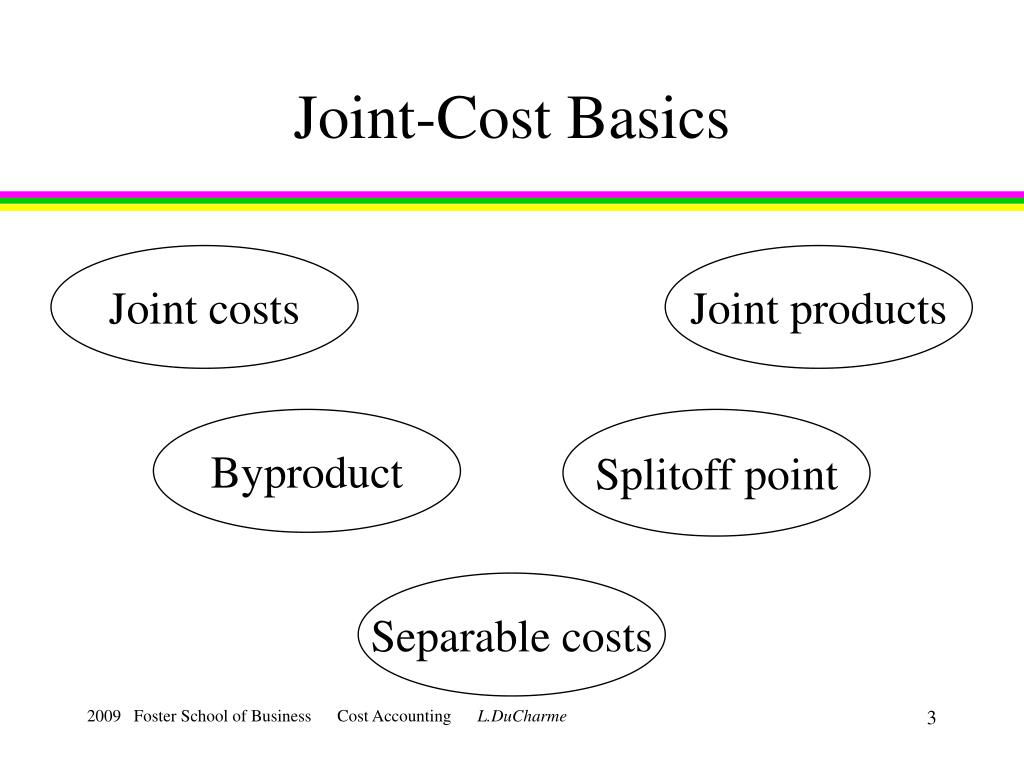
Joint costs are production costs incurred in creating two (or more) products. The splitoff point is the point when the costs of two or more products can be separately identified. After splitoff, each product incurs separable (or independent) costs. Figure a product's total cost in cost accounting.

Joint Costs Allocation using the Physical Units Method (Cost Accounting
Definition: Joint costs are costs that are incurred from buying or producing two products at the same time. In cost accounting terms, joint costs have the same cost object. What Does Join Cost Mean? Manufacturers incur many costs in the production process.It is the cost accountant's job to trace these costs back to a certain product or process (cost object) during production.
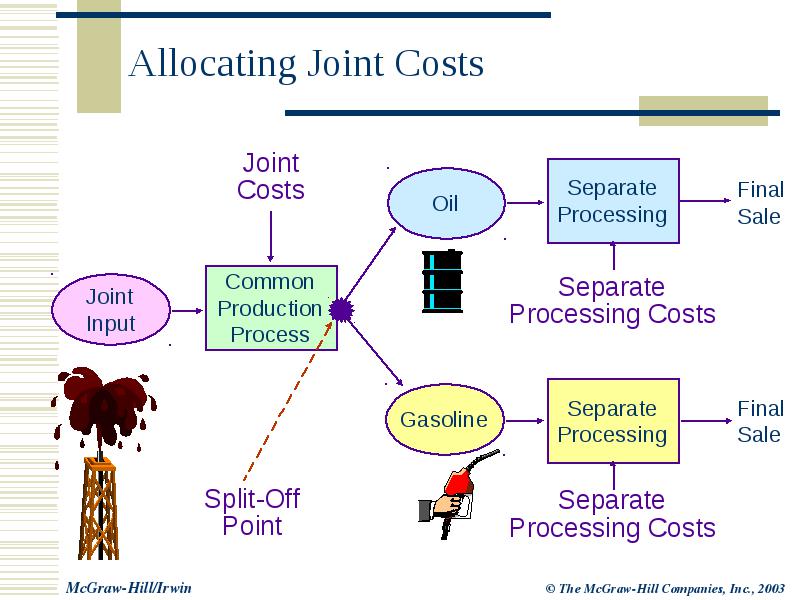
Cost Accumulation, Tracing, and Allocation Chapter 5 Introduction
Joint Cost. Joint cost is the cost that incurs during the production of multiple products at the same time. It is the cost that require to produce the joint products. The production requires similar raw material, but result in multiple products type. We will not be able to separate the joint cost until the split-off point.

PPT Cost Allocation Joint Products and Byproducts PowerPoint
Joint Cost = C/U. Where, C = Total cost of joint products. U = Total units produced. Another method to calculate the joint cost function is the survey method. Under this method, other factors such as material quality, marketing, and selling price are also considered. In totality, both qualitative and quantitative measures are considered before.

PPT Cost Allocation Departments, Joint Products, and ByProducts
Joint cost and oil industry. The oil industry is well known for using joint cost accounting. The oil filtration business processes the crude oil to produce petrol, gasoline, and higher octane, etc from a single resource consumed. Hence, the cost incurred on the purchase of crude oil is a joint cost that needs to be allocated.
PPT Cost Allocation Joint Products and Byproducts PowerPoint
Joint Cost. The expense incurred by producers when creating more than one product or process is referred to as the joint cost. These costs include labor, materials, and overhead for the joint product's manufacture. Almost every manufacturer uses joint cost allocation to keep input costs under control.